UN Beyond-GDP Process
The coming years are going to be exciting times for the Beyond GDP community. The United Nations (UN) is in a process of discussing a framework to go beyond GDP.
Now is the time to correct a glaring blind spot in how we measure economic prosperity and progress. When profits come at the expense of people and our planet, we are left with an incomplete picture of the true cost of economic growth.
Valuing What Counts
The foundation for the UN Beyond-GDP process, is the “Valuing What Counts – United Nations System-wide Contribution on Progress Beyond Gross Domestic Product (GDP)”. The UN aims to identify metrics that are as clear and appealing as GDP, but more inclusive of environmental and social aspects of progress, with the goal of changing the focus of policymaking towards more sustainable, just and inclusive development. The aim is not to establish one complex, composite indicator of Beyond GDP, because “an indicator of everything would summarise too much and reveal too little”. More targeted information will be needed. Therefore, the UN system proposes a set of core metrics, limited to a maximum of 10 to 20 strong headline indicators.
First, a process will be executed to agree politically on the issues at stake, targets and commitment to action. After that, a comprehensive process of indicator selection will be launched. The current planning is that Member States’ deliberations will be taking place from now until the Summit of the Future in September 2024. This Summit could then launch a technical process to identify and develop metrics for the Beyond GDP framework reflecting on the deliberations.
If the United Nations are to deliver on our promises to future generations – to secure a world where everyone can thrive in peace, dignity, and equality on a healthy planet – the international community needs to reshape the foundations and reaffirm the core values that underpin collective action. This applies to the functioning of our economies as well.
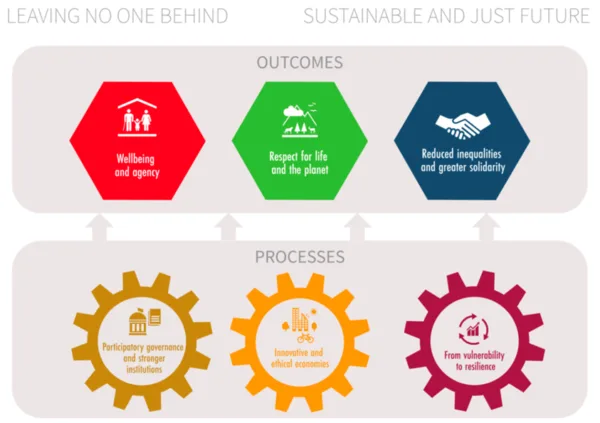
The Conceptual Framework
The framework proposed by the UN in the paper “Valuing What Counts” consists of three outcome elements and three process elements (see Figure 1). The three outcome elements are derived from the Brundtland Report and the SDGs. They are:
- ‘wellbeing and agency’ to focus on wellbeing now;
- ‘respect for life and the planet’ to ensure possibilities for life and wellbeing in the future; and
- ‘reduced inequalities and greater solidarity’ towards a more equal distribution of wellbeing
The three process elements are:
- ‘from vulnerability to resilience’ to focus on our interaction with the natural built environment to strengthen our preparedness and ensure the conditions for wellbeing given multiple risks;
- ‘participatory governance and stronger institutions’ to steer us towards the outcomes ensuring equal and safe societal conditions empowering everyone to contribute;
- ‘innovate and ethical economies’ to serve people and societies by thriving innovation to find solutions to our challenges with responsible and ethical actions that expand the capacity to coordinate and deliver positive outcomes.
The three formulated outcomes of the UN's conceptual framework are the same as the three elements of WISE - wellbeing (wellbeing today), inclusion (wellbeing for all) and sustainability (wellbeing in the future). We hope that the alignment of the UN's framework and this webpage, will help the global deliberations.
Revision of the System of National Accounts
The System of National Accounts (SNA) is the internationally agreed standard set of recommendations on how to compile measures of economic activity. It can be considered a UN success story as national statistical offices over the whole word use it to produce reliable, consistent, comparable, and replicable national accounts. The national accounts are one of the building blocks of macroeconomic statistics, most notably GDP, forming a basis for economic analysis and policy formation.
The current SNA handbook dates from 2008. The UN are working on a revision towards the renewed 2025 SNA. The update and extension is focusing on issues of digitalisation, globalisation, wellbeing and sustainability, distributional aspects and informal economy, including unpaid work. The SNA extensions will underpin the development of a framework and metrics for Beyond GDP. It could form an expended SNA framework or contribute to the development of a network of frameworks that could provide the source of many strong headline indicators to complement GDP and enable broadened national wealth concepts to address sustainability.
You can find more information in the UN paper “Valuing What Counts – United Nations System-wide Contribution on Progress Beyond Gross Domestic Product (GDP)” and on the SNA revision website.
